The triple constraint is the framework which evaluates the relationship between three primary variables in any project - time, cost and scope. These three variable are interdependent. All projects are limited in some way by these three constraints. The relationship between these variables is such that if any one of the three factors change, at least one other factor is likely to be affected. Project management is the science of making intelligent trade-offs between time, cost and scope. All three of the factors combined determine a project's quality.
2. Describe the two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning
The two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning are PERT and Gantt chart.
PERT chart - is a graphical network model that depicts a project's tasks and the relationships between those tasks. PERT charts define dependency between project tasks before tasks are scheduled. PERT charts frequently display a projects critical path.
An e.g. PERT chart
Gantt chart - simple bar chart that depicts project tasks against a calender. In a Gantt chart, tasks are listed vertically and the project's time frame is listed horizontally. It shows actual progress of tasks against the planned duration
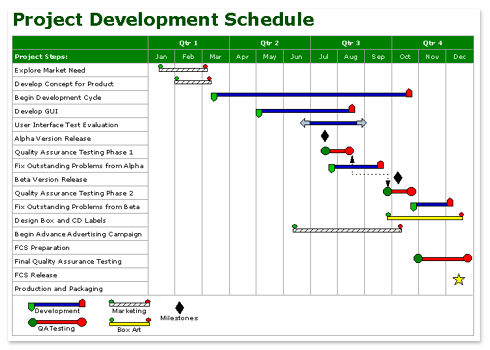.gif)
e.g. Gantt Chart
3. Identify the three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success
The three primary areas a project manager must focus on to ensure success, include:
- Managing People - Being able to resolve conflict within the team and balancing the needs of the project. As such communication, negotiation, marketing and salesmanship are just as important
- Managing communication - project manager distributes timely, accurate and meaningful information regarding project objectives that involve time, cost, scope and quality. Another important aspect of communication is receiving feedback
- Managing change - Successful organisations and successful people learn to anticipate and react appropriately to change
2 reason why projects fail include:
- length of contract - most contracts have long contracts this is because of high cost of transferring assets. It cause difficulties to get out of contract, problems reforming IT department
- Increase competitors
- increase in quality and efficiency of a process, service or function
- access to advanced technologies, reduced operating costs


.gif)